1Clinical Applications of Cardiac Bio-markers. IFCC: International Federation of Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine, 26 July 2014. Web. 14 Feb. 2017.
2Storrow, AB et al. Diagnostic Performance of Cardiac Troponin I For Early Rule-in and Rule-out of Acute Myocardial Infarction: Results of a Prospective Multicenter Trial. Clinical Biochemistry, 2015; 48:254-259.
3Thygesen K, Mair J, Giannitsis E, Mueller C, Lindahl B, Blankenberg S, et al. How to use high-sensitivity cardiac troponins in acute cardiac care. Eur Heart J 2012; 33: 2252-7. Korley FK, Jaffe AS. Preparing the United States for high-sensitivity cardiac troponin assays. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2013; 61:1753-8.
42015 ESC guidelines for the management of acute coronary syndromes in patients presenting without persistent ST-segment elevation. http://eurheartj.oxfordjournals.org. Last accessed on January 19, 2017.
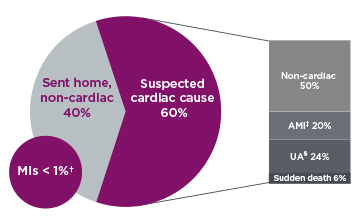
*Figure 1: Adapted and used with permission from W. Frank Peacock, M.D., FACEP Baylor College of Medicine.
†1% = 50,000 MIs after patient was sent home.
‡AMI = Acute Myocardial Infarction.
§UA = Unstable Angina.
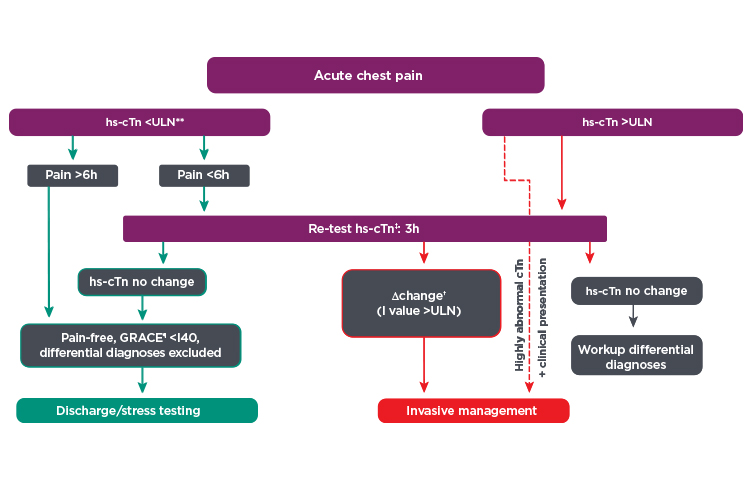
¶GRACE = Global Registry of Acute Coronary Events score.
**ULN = upper limit of normal, 99th percentile of healthy controls.
††Δ change, dependent on assay. Highly abnormal hsTn defines values beyond 5-fold the upper limit of normal.
‡‡hs-cTn = high sensitivity cardiac troponin.
 English
English