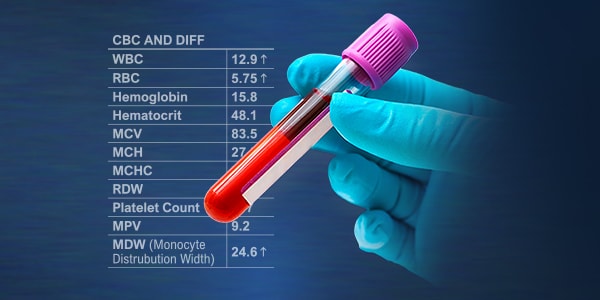
Hematological Biomarker in the Emergency Department
Monocyte Distribution Width (MDW) is a measure of increased morphological variability of monocytes in response to bacterial, viral or fungal infections. The quantitative analysis of MDW has received regulatory-clearance as an aid in identifying risk of severe infection and sepsis in adult patients in the ED.
Considered with other signs and symptoms, the value of MDW helps differentiate sepsis from non-septic presentations, including non-infectious systemic inflammatory response.4 This parameter is available early in patient assessment as part of a complete blood count with differential test (CBC-diff), with no impact to workflow.
What Makes Monocyte Distribution Width Unique?
Regulatory-Cleared
MDW is the only regulatory-cleared hematological biomarker that helps to establish risk of severe infection and sepsis in adult ED patients.
Reduce Dx Uncertainty
MDW helps reduce diagnostic uncertainty. It is available early to help clinicians escalate or de-escalate care in patients with suspected infectious etiology.
Enhanced CBC-Diff
MDW is available early in patient assessment as a part of a CBC-diff, no impact to workflow.
Latest News
ArticleBecker Health
Understanding the host’s response to infection is key to early identification of sepsis. In this article, Host Response in Sepsis: New Tools for Diagnosis and Management of Infectious Disease, Learn how the integration of the next generation of diagnostic tools is changing the trajectory of this deadly syndrome.
ArticleACEP
In the latest installment of “Conversations with Industry,” from the American College of Emergency Physicians, MDW is the topic of focus for sepsis identification in the ED. Dr. Nima Sarani, from the University of Kansas Medical Center, discusses the latest evidence and practical utility of MDW.
PodcastSAEM
New Society for Academic Emergency Medicine podcast series, “Current and Novel Approaches to Sepsis Detection in the ED.” SAEM Research and EMTIDE Interest Group members and academic emergency medicine providers discuss best practices for early sepsis identification and improved patient outcomes and the research surrounding biomarkers in an acute clinical setting.
MDW Patient Case Studies
Training Clinical Introduction to MDW Parameter for Your ED
In this presentation, Melissa Naiman, PhD, EMT-B shares the fundamentals of Monocyte Distribution Width (MDW) and explains the clinical utility of incorporating the MDW biomarker as part of the complete blood count with differential (CBC-diff) early in ED screening to aid in identifying risk of severe infection and sepsis in your emergency department.
Watch videoLatest Scientific Presentations
Peer-Reviewed Studies
MDW has been studied for the past decade with more than 60 peer-review publications and over 30,000+ patients.6-16, confirming the robustness and reproducibility of MDW performance in different patient populations. View these peer-reviewed studies to learn about the clinical utility of MDW.
Peer-Reviewed Clinical Study Critical Care Medicine Study
Discover how a multicenter study validated MDW as a novel indicator for Sepsis-2 and Sepsis-3 in high-risk emergency department patients.
Read studyPeer-Reviewed Clinical Study PLOS ONE Study
Research shows MDW compared with C-reactive protein and procalcitonin (PCT) for early sepsis detection in the ED.
Read studyPeer-Reviewed Clinical Study Journal of Intensive Care
New analysis from a pivotal study shows that patients with abnormal MDW values at presentation have increased odds of sepsis.
Read studyPeer-Reviewed Clinical Study American College of Chest Physicians Study
Clinical research shows that MDW adds value to WBC count for early sepsis detection in the ED.
Read studyAdditional Resources
-
Access PCT Assay
Find out more -
MeMed BV® Bacterial Viral Immunoassay
Learn more -
Host Response to Infection
Learn more -
Monocyte Distribution Width
Find out more
1. Rudd, et al., Lancet. 2020 Jan 18; 395 (10219): 200-211.
2. Torio C, Moore B. “National Inpatient Hospital Costs: The Most Expensive Conditions by Payer.” www.hcup-us.ahrq.gov/reports/statbriefs/sb204-Most-Expensive-Hospital-Conditions.pdf, May 2016. Accessed 15 Jan. 2018.
3. Filbin, M. R., Lynch, J., Gillingham, T. D., Thorsen, J. E., Pasakarnis, C. L., Nepal, S., et al. Presenting Symptoms Independently Predict Mortality in Septic Shock. Critical Care Medicine, 2018; 46(10), 1592-1599. https://doi.org/10.1097/ccm.0000000000003260.
4. UniCel DxH 900 Coulter Cellular Analysis System Early Sepsis Indicator (ESId) Application AddendumPN C42014AA.
5. Sepsis Pivotal Repository PN C54726 Rev. AB located in CPDM.
6. Malinovska, A et al., Monocyte distribution width as part of a broad pragmatic sepsis screen in the emergency department. JACEP Open. 2022; 3:e12679. https://doi.org/10.1002/emp2.12679
7. E. Piva et al., Monocyte Distribution Width (MDW) Parameter as a Sepsis Indicator in Intensive Care Units, Clin Chem Lab Med 2021. https://doi.org/10.1515/cclm-2021-0192
8. P. Hausfater et al., Monocyte Distribution Width (MDW) Performance as an Early Sepsis Indicator in the Emergency Department: Comparison with CRP and Procalcitonin in a Multicenter International European Prospective Study, Crit Care 2021; 25, 227. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13054-021-03622-5
9. A. Woo et al., Monocyte Distribution Width Compared with C-Reactive Protein and Procalcitonin for Early Sepsis Detection in the Emergency Department, PLoS ONE 2021; 16(4): e0250101. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0250101
10. H. Lin et al., Clinical Impact of Monocyte Distribution Width and Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio for Distinguishing COVID-19 and Influenza from Other Upper Respiratory Tract Infections: A Pilot Study, PLoS ONE 2020 15(11): e0241262. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0241262
11. L. Agnello et al., Monocyte Distribution Width (MDW) as a Screening Tool for Sepsis in the Emergency Department, Clin Chem Lab Med 2020; 58(11):1951-1957. https://doi:10.1515/cclm-2020-0417
12. G. Riva et al., Monocyte Distribution Width (MDW) as Novel Inflammatory Marker with Prognostic Significance in COVID 19 Patients, Scientific Report 2021; 11:12716. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-92236-6
13. Marcos-Morales, A et al., Elevated monocyte distribution width in trauma: An early cellular biomarker of organ dysfunction, Injury 2021; S0020-1383(21):00933-00935. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2021.11.026
14. E. Crouser et al., Monocyte Distribution Width: A Novel Indicator of Sepsis-2 and Sepsis-3 in High-Risk Emergency Department Patients, Critical Care Med 2019; 47:1018-1025. https://doi.org/10.1097/CCM.0000000000003799
15. E. Crouser et al., Improved Early Detection of Sepsis in the ED with a Novel Monocyte Distribution Width Biomarker, CHEST 2017; 152(3):518-526. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chest.2017.05.039
16. A. Ognibene et al., Elevated Monocyte Distribution Width in COVID-19 Patients: The Contribution of the Novel Sepsis Indicator, Clinica Chimica Acta 2020; 509: 22-24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2020.06.002
 English
English